

Although the attachments appear to be common file kinds like *.doc or *.pdf, they have a disguised executable (*.exe) with a double extension. Infection Risks and Common Infection MethodsĮmails containing unknown attachments are the most typical route of infection.
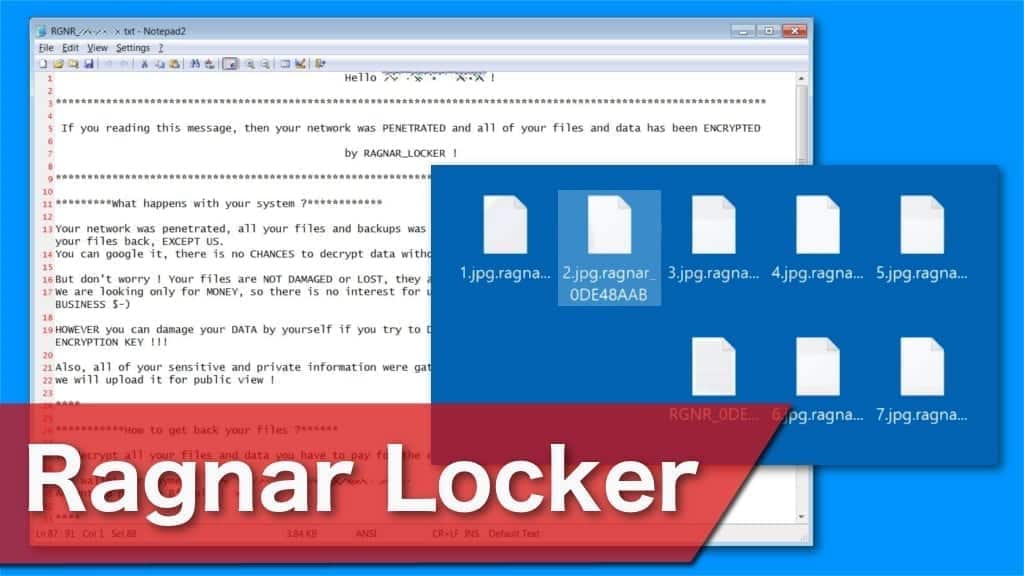
The encryption procedure can take several hours, giving CryptoLocker some time to "incubate" before causing symptoms on the victim's PC. It encrypts your data and then displays a ransom letter notifying you that you must pay a ransom to get your files back.ĬryptoLocker initially installs itself in the user's profile before scanning the machine, any connected devices, and any other network devices for files and folders to encrypt. The ransomware operators like CryptoLocker keep both keys, including the private key that you'll need to decrypt your files.ĬryptoLocker acts similarly to other modern ransomware after it's installed on your PC. When using asymmetric encryption with the above purposes, such as transferring sensitive material, the receiver gives the sender the public key to encrypt the data but keeps the private key. This two-key system encrypts using one public key and decrypts with another, both of which are linked to each other. How does it work?ĬryptoLocker employs a difficult-to-crack asymmetric encryption technology. However, there are now internet tools that claim to decrypt CryptoLocker-encrypted files. Users without dependable backups had the option of paying the ransom and hoping that those behind the infection were honest enough to really decrypt the impacted files or simply acknowledging their data as lost at the time of the original outbreak. While the infection is not difficult to eradicate, the data that have been infected stay encrypted. It then demands a ransom to decrypt or retrieve the system owner's impacted files If you don't, your private key will be lost. It looks for particular file types to encrypt using RSA public-key cryptography after being downloaded and activated and then delivers the private key to specified remote sites. Infected email attachments or a botnet propagates CryptoLocker. It originally appeared on the Internet in 2013 and was designed to infect PCs running Windows. CryptoLocker is a ransomware Trojan that supposedly encrypts files on a victim's computer and demands a fee to retrieve the data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
